Page 64 - JBO-Katalog-2022
P. 64
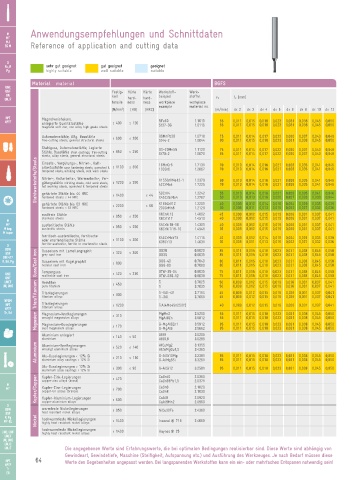
M Anwendungsempfehlungen und Schnittdaten
MF
MJ
EG M Reference of application and cutting data
G
Rc, R sehr gut geeignet gut geeignet geeignet
Pg highly suitable well suitable suitable
Material material BGFS
UNC
UNF Festig- Härte Härte Werkstoff- Werk-
UN keit beispiel stoffnr.
UNJF hard- hard- vc fz [mm]
tensile ness ness workpiece workpiece
example material no.
[N/mm ] 2 [HB] [HRC] [m/min] d≤ 2 d≤ 3 d≤ 4 d≤ 5 d≤ 6 d≤ 8 d≤ 10 d≤ 12
NPT Magnetweicheisen,
NPTF unlegierte Qualitätsstähle ≤ 400 ≤ 120 RFe60 1.1015 85 0,011 0,015 0,018 0,023 0,031 0,038 0,045 0,050
magnetic soft iron, non alloy high grade steels St37-3G 1.0116 85 0,011 0,015 0,018 0,023 0,031 0,038 0,045 0,050
Automatenstähle, Allg. Baustähle ≤ 600 ≤ 200 9SMnPb28 1.0718 75 0,011 0,014 0,017 0,022 0,030 0,037 0,043 0,048
free-cutting steels, general structural steels St44-2 1.0044 80 0,011 0,015 0,018 0,023 0,031 0,038 0,045 0,050
Stahlguss, Automatenstähle, Legierte GS-20Mn5N 1.1120 75 0,011 0,014 0,017 0,022 0,030 0,037 0,043 0,048
Stähle, Baustähle steel castings, free-cutting ≤ 850 ≤ 250 St70-2 1.0070 65 0,011 0,014 0,017 0,022 0,030 0,037 0,043 0,048
steels, alloy steels, general structural steels ≤ 350 16MnCr5 1.7131 70 0,010 0,014 0,016 0,021 0,028 0,035 0,041 0,046
Stahlwerkstoffe/Steels tempered steels, nitriding steels, cold work steels ≥ 350 100Cr6 1.2067 70 0,010 0,014 0,016 0,021 0,028 0,035 0,041 0,046
Einsatz-, Vergütungs-, Nitrier-, Kalt-
arbeitsstähle case hardening steels, quenched & ≤ 1100
Nitrier-, Kaltarbeits-, Warmarbeits-, Ver-
0,010 0,014 0,016 0,021 0,028 0,035 0,041 0,046
60
1.2379
X155CrVMo12-1
gütungsstähle nitriding steels, cold work steels, ≥ 1200
0,035
0,016
70
0,014
0,021
0,046
0,028
1.7225
0,041
0,010
42CrMo4
hot working steels, quenched & tempered steels
gehärtete Stähle bis 44 HRC
0,020
0,013
X45CrNiMo4
0,044
50
0,033
0,016
0,039
0,027
hardened steels ≤ 44 HRC
0,010
1.2767
X165CrV12
1.2201
40
0,009 0,012 0,014 0,018 0,024 0,029 0,035 0,039
gehärtete Stähle bis 63 HRC ≤ 1400 ≤ 44 59CrV4 1.2242 55 0,010 0,014 0,016 0,021 0,028 0,035 0,041 0,046
≤ 66
≤ 2200
hardened steels ≤ 63 HRC 200CrMn8 1.2129 30 0,008 0,011 0,013 0,016 0,022 0,027 0,032 0,036
rostfreie Stähle ≤ 850 ≤ 250 X6CrAl13 1.4002 45 0,009 0,012 0,015 0,019 0,026 0,031 0,037 0,041
M stainless steels X6CrTi17 1.4510 40 0,009 0,012 0,015 0,019 0,026 0,031 0,037 0,041
MF austenitische Stähle X5CrNi18-10 1.4301 40 0,009 0,012 0,015 0,019 0,026 0,031 0,037 0,041
M keg. austenitic steels ≤ 850 ≤ 250 X6CrNiTi18-10 1.4541 35 0,009 0,012 0,015 0,019 0,026 0,031 0,037 0,041
M taper
ferritisch-austenitische, ferritische X45CrMoV15 1.4116 40 0,009 0,012 0,014 0,018 0,024 0,029 0,035 0,039
oder martensitische Stähle ≤ 1100 ≤ 300 X38Cr13 1.4031 30 0,008 0,011 0,013 0,016 0,022 0,027 0,032 0,036
G ferritic-austenitic, ferritic or martensitic steels
BSW Gusseisen mit Lamellengraphit GG20 0.6020 85 0,011 0,015 0,018 0,023 0,031 0,038 0,045 0,050
BSF grey cast iron ≤ 320 ≤ 300 GG35 0.6035 85 0,011 0,015 0,018 0,023 0,031 0,038 0,045 0,050
DIN 477
R, BA, Pg Guss/Cast iron Gusseisen mit Kugelgraphit ≤ 800 GGG-40 0.7040 80 0,011 0,015 0,018 0,023 0,031 0,038 0,045 0,050
0,015
0,023
0,018
0,050
GGG-80
0,011
0.7080
0,045
0,038
80
nodular cast iron
0,031
UNC Temperguss ≤ 420 ≤ 230 GTW-35-04 0.8035 75 0,011 0,015 0,018 0,023 0,031 0,038 0,045 0,050
0,045
75
0,031
0,023
0,011
0,015
0,018
0,050
0,038
0.8038
GTW-S38-12
malleable cast iron
UNF
UNEF Reintitan Ti 3.7025 50 0,009 0,012 0,015 0,019 0,026 0,031 0,037 0,041
UN, UNS pure titanium ≤ 450 Ti 3.7035 50 0,009 0,012 0,015 0,019 0,026 0,031 0,037 0,041
3.7164
45
0,009 0,012 0,015 0,019 0,026 0,031 0,037 0,041
Ti-6Al-4V
Titanlegierungen
NPSM Titan/Titanium titanium alloys ≤ 900 Ti-3Al 3.7065 45 0,009 0,012 0,015 0,019 0,026 0,031 0,037 0,041
NPT Titanlegierungen ≤ 1200 TiAl4Mo4Sn2Si0.5 40 0,009 0,012 0,015 0,019 0,026 0,031 0,037 0,041
titanium alloys
NPTF
Tr, Rd Magnesium-Knetlegierungen ≤ 310 MgMn2 3.5200 85 0,011 0,015 0,018 0,023 0,031 0,038 0,045 0,050
Magnesium wrought magnesium alloys ≤ 170 MgAl8Zn 3.5812 85 0,011 0,015 0,018 0,023 0,031 0,038 0,045 0,050
G-MgAl8Zn1
85
0,011 0,015 0,018 0,023 0,031 0,038 0,045 0,050
3.5912
Magnesium-Gusslegierungen
0,015
85
0,050
0,045
0,038
0,011
0,023
0,031
0,018
cast magnesium alloys
G-MgAl6
3.5662
Aluminium unlegiert ≤ 140 ≤ 50 Al99 3.0205
aluminium Al99,8 3.0285
Aluminium wrouhgt aluminium alloys ≤ 520 ≤ 140 AlZnMgCu1,5 3.4365 85 0,011 0,015 0,018 0,023 0,031 0,038 0,045 0,050
3.1355
AlCuMg2
Aluminium-Knetlegierungen
G-AlSi10Mg
Alu-Gusslegierungen < 12% Si
3.2381
≤ 210
≤ 110
0,045
0,050
0,038
0,031
0,023
aluminium alloy castings < 12% Si
0,018
85
0,015
3.3261
G-AlMg5Si
0,011
Alu-Gusslegierungen > 12% Si ≤ 300 ≤ 90 G-AlSi12 3.2581 85 0,011 0,015 0,018 0,023 0,031 0,038 0,045 0,050
aluminium alloy castings > 12% Si CuZn40 2.0360
Kupfer/Copper copper-tin alloys (bronze) CuSn8 2.1030
Kupfer-Zink-Legierungen
M copper-zinc alloys (brass) ≤ 470 CuZn38Pb1,5 2.0371
MF Kupfer-Zinn-Legierungen ≤ 700 CuSn6 2.1020
CuAl9Mn2
2.0960
copper-aluminium alloys
G Kupfer-Aluminium-Legierungen ≤ 600 CuAl8 2.0920
BSW warmfeste Nickellegierungen ≤ 850 NiCu30Fe 2.4360
BSF heat resistant nickel alloys
R, Pg hochwarmfeste Nickellegierungen
MF-EL Nickel highly heat resistant nickel alloys ≤ 1400 Inconel ® 718 2.4668
hochwarmfeste Nickellegierungen
UNC, UNF highly heat resistant nickel alloys ≤ 1400 Haynes ® 25
UNEF
UN, UNS
UNJC
UNJF Die angegebenen Werte sind Erfahrungswerte, die bei optimalen Bedingungen realisierbar sind. Diese Werte sind abhängig von
Gewindeart, Gewindetiefe, Maschine (Steifigkeit, Aufspannung etc.) und Ausführung des Werkzeuges. Je nach Bedarf müssen diese
NPT 64 Werte den Gegebenheiten angepasst werden. Bei langspanenden Werkstoffen kann ein ein- oder mehrfaches Entspanen notwendig sein!
NPTF
Tr
EG