Page 142 - JBO-Katalog-2022
P. 142
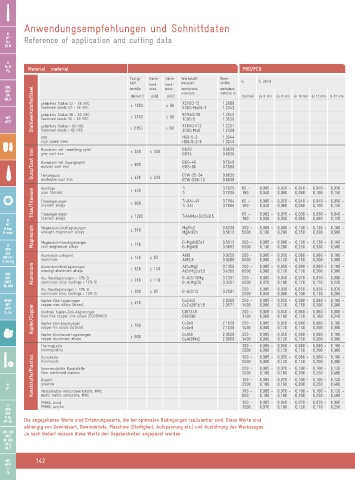
Anwendungsempfehlungen und Schnittdaten
M
MF Reference of application and cutting data
MJ
EG M
G
Rc, R Material material PKD/PCD
Pg
Festig- Härte Härte Werkstoff- Werk-
keit hard- hard- beispiel stoffnr. vc fz [mm]
UNC tensile ness ness workpiece workpiece
Stahlwerkstoffe/Steel hardened steels 52 - 56 HRC ≤ 1950 ≤ 56 X38CrMoV5-1 1.2343
UNF example material no.
UN [N/mm ] 2 [HB] [HRC] [m/min] d≤ 6 mm d≤ 8 mm d≤ 10 mm d≤ 12 mm d> 12 mm
UNJF gehärtete Stähle 52 - 56 HRC X210Cr12 1.2080
NPT gehärtete Stähle 56 - 60 HRC ≤ 2150 ≤ 60 90MnCrV8 1.2842
1.3505
100Cr6
hardened steels 56 - 60 HRC
NPTF gehärtete Stähle > 60 HRC > 2150 > 60 X165CrV12 1.2201
hardened steels > 60 HRC
HS6-5-3
1.3344
HSS 200CrMn8 1.2129
high speed steel ≤ 320 ≤ 300 HS6-5-2-5 1.3243
0.6020
GG20
Gusseisen mit Lamellengraphit
Guss/Cast iron grey cast iron ≤ 800 ≤ 230 GG35 0.6035
0.7040
GGG-40
Gusseisen mit Kugelgraphit
nodular cast iron
0.7080
GGG-80
GTW-35-04
0.8035
Temperguss
≤ 420
GTW-S38-12
0.8038
malleable cast iron
Titan/Titanium Reintitan ≤ 450 Ti 3.7025 60 - 0,005 - 0,020 - 0,040 - 0,040 - 0,050 -
0,080
pure titanium
0,040
0,150
0,060
3.7035
Ti
0,100
180
3.7164 60 -
Ti-6Al-4V
0,005 - 0,020 - 0,040 - 0,040 - 0,050 -
Titanlegierungen
≤ 900
titanium alloys
0,060
0,100
0,150
Ti-3Al
0,080
180
3.7065
0,040
0,050
0,080
0,060
180
0,030
0,120
titanium alloys
M Titanlegierungen ≤ 1200 TiAl4Mo4Sn2Si0.5 60 - 0,002 - 0,015 - 0,030 - 0,030 - 0,040 -
MF
M keg. Magnesium-Knetlegierungen ≤ 310 MgMn2 3.5200 300 - 0,005 - 0,080 - 0,130 - 0,130 - 0,160 -
M taper Magnesium wrought magnesium alloys MgAl8Zn 3.5812 5000 0,130 0,200 0,250 0,330 0,500
G Magnesium-Gusslegierungen ≤ 170 G-MgAl8Zn1 3.5912 300 - 0,005 - 0,080 - 0,130 - 0,130 - 0,160 -
0,130
0,500
5000
0,330
0,200
3.5662
0,250
G-MgAl6
cast magnesium alloys
BSW
BSF Aluminium unlegiert Al99 3.0205 200 - 0,005 - 0,050 - 0,080 - 0,080 - 0,100 -
DIN 477 aluminium ≤ 140 ≤ 50
R, BA, Pg Aluminium-Knetlegierungen Al99,8 3.0285 6000 0,080 0,120 0,150 0,200 0,300
0,005 - 0,050 - 0,080 - 0,080 - 0,100 -
3.1355 200 -
AlCuMg2
UNC Aluminium wrouhgt aluminium alloys ≤ 520 ≤ 140 AlZnMgCu1,5 3.4365 6000 0,080 0,120 0,150 0,200 0,300
UNF Alu-Gusslegierungen < 12% Si ≤ 210 ≤ 110 G-AlSi10Mg 3.2381 200 - 0,005 - 0,040 - 0,070 - 0,070 - 0,080 -
UNEF aluminium alloy castings < 12% Si G-AlMg5Si 3.3261 4000 0,070 0,100 0,120 0,170 0,250
UN, UNS
Alu-Gusslegierungen > 12% Si ≤ 300 ≤ 90 G-AlSi12 3.2581 200 - 0,005 - 0,030 - 0,050 - 0,050 - 0,070 -
aluminium alloy castings > 12% Si 2000 0,050 0,080 0,100 0,130 0,200
NPSM Kupfer-Zink-Legierungen ≤ 470 CuZn40 2.0360 250 - 0,005 - 0,050 - 0,080 - 0,080 - 0,100 -
NPT copper-zinc alloys (brass) CuZn38Pb1,5 2.0371 1400 0,080 0,120 0,150 0,200 0,300
Kupfer/Copper Kupfer-Zinn-Legierungen ≤ 700 C69300 2.1020 250 - 0,060 0,100 0,120 0,160 0,240
NPTF
Tr, Rd bleifreie Kupfer-Zink-Legierungen CW724R 200 - 0,005 - 0,040 - 0,060 - 0,060 - 0,080 -
1100
lead free copper zink alloys (ECOBRASS)
0,005 - 0,050 - 0,080 - 0,080 - 0,100 -
CuSn6
0,300
0,080
0,120
1400
CuSn8
0,150
copper-tin alloys (bronze)
0,200
2.1030
Kupfer-Aluminium-Legierungen
0,300
0,080
CuAl9Mn2
0,150
0,200
1400
copper-aluminium alloys ≤ 600 CuAl8 2.0920 250 - 0,005 - 0,050 - 0,080 - 0,080 - 0,100 -
2.0960
0,120
Thermoplaste 100 - 0,005 - 0,050 - 0,080 - 0,080 - 0,100 -
thermoplatics 2500 0,080 0,120 0,150 0,200 0,300
100 -
0,005 - 0,050 - 0,080 - 0,080 - 0,100 -
Kunststoffe/Plastics faserverstärkte Kunststoffe 200 - 0,005 - 0,070 - 0,100 - 0,100 - 0,120 -
Duroplaste
2500
0,300
0,120
thermosets
0,150
0,200
0,080
0,250
0,100
fiber reinforced plastics
0,160
0,200
0,400
3000
150 -
0,005 - 0,070 - 0,100 - 0,100 - 0,120 -
Graphit
M graphite 2500 0,100 0,160 0,200 0,250 0,400
MF Metallmatrix-Verbundwerkstoffe, MMC 150 - 0,005 - 0,070 - 0,100 - 0,100 - 0,120 -
0,200
0,400
0,250
0,100
800
metal matrix composite, MMC
0,160
PMMA, Acryl 100 - 0,005 - 0,040 - 0,070 - 0,070 - 0,080 -
G PMMA, acrylic 1200 0,070 0,100 0,120 0,170 0,250
BSW
BSF
R, Pg
MF-EL Die angegebenen Werte sind Erfahrungswerte, die bei optimalen Bedingungen realisierbar sind. Diese Werte sind
abhängig von Gewindeart, Gewindetiefe, Maschine (Steifigkeit, Aufspannung etc.) und Ausführung des Werkzeuges.
UNC, UNF Je nach Bedarf müssen diese Werte den Gegebenheiten angepasst werden.
UNEF
UN, UNS
UNJC
UNJF
NPT 142
NPTF
Tr
EG